Ideas need money to move. You may have talent as well as clarity. You may even have a great team. But without funding, growth slows down. Development stops. Opportunities are missed. This is why many good ideas never become great companies. Money is not the goal of a startup. But money is the fuel.
Understanding types of business funding is not just for investors or finance experts. It is a basic survival skill for founders. Each funding stage exists for a reason. Each stage supports growth. When founders understand this journey, they can make better decisions and avoid mistakes.
Why Understanding Funding Stages Matters
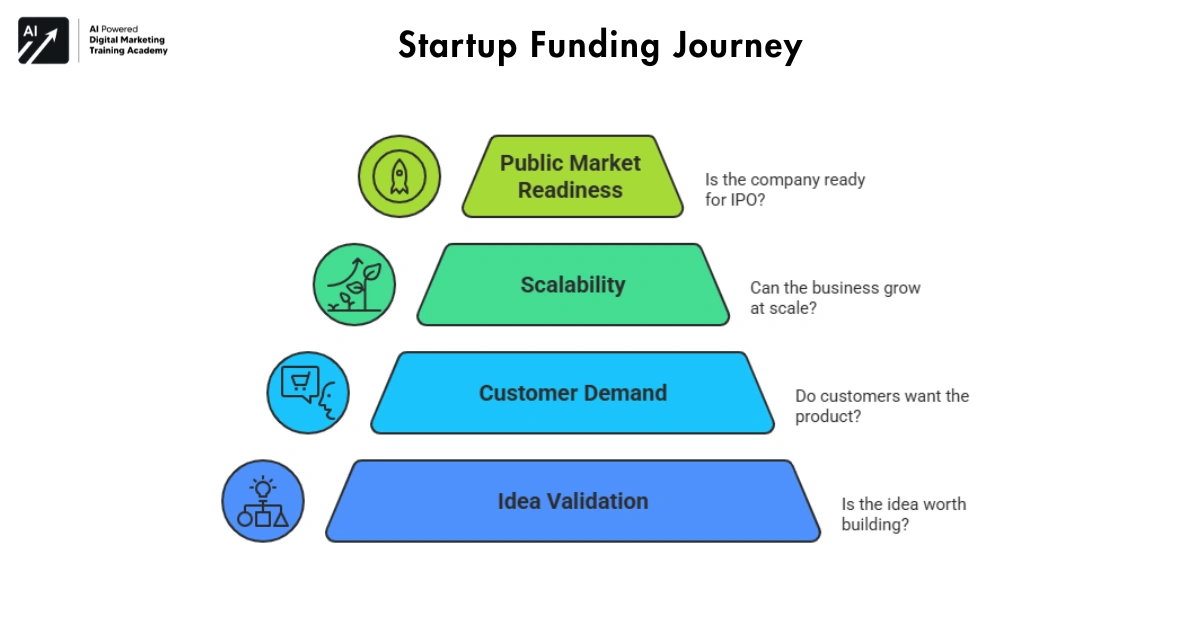
Startup funding is not one big event. It is a journey. From this idea to IPO, startups pass through multiple stages of funding.
Each stage answers a different question:
- Is this idea worth building?
- Do customers actually want this product?
- Can this business grow at scale?
- Is this company ready for the public market?
When founders don’t understand the funding stages, they may raise money at the wrong time, from the wrong people, or for the wrong reasons. This creates pressure, dilution, and sometimes failure.
Understanding funding stages helps you:
- Raise money only when needed
- Choose the right type of investor
- Protect ownership and control
- Align money with growth goals
Common Funding Mistakes Founders Make
Most founders are not bad decision-makers.They are just uninformed. Here are some common mistakes founders make when it comes to funding:
Raising money too early
Some founders chase funding before validating their idea. They think money will fix everything. In reality, money only amplifies what already exists. If the idea is weak, funding makes the failure bigger and faster.
Raising money too late
Other founders delay funding too much. They bootstrap beyond their limits, miss growth opportunities, and burn out. Funding exists to support growth not to be avoided out of fear.
Choosing the wrong investors
Not only all money is good money. Sometimes investors bring pressure, misalignment, or unrealistic expectations. Smart founders choose investors who understand their stage and vision.
Not understanding dilution
Many beginners don’t realize how much ownership they give away. They focus on valuation, not long-term control. Over time, this leads to regret and loss of decision power.
Treating funding as success
Funding is not success. Customers are. Revenue is. Impact is. Funding is just a tool not the finish line. Avoiding these mistakes starts with one thing: clarity about funding stages.
Pre-Seed Funding Stage From Idea to First Prototype
Every startup begins before it becomes a company.This very early phase is called the pre-seed stage. At this stage, you don’t have revenue. You do not need to have a product. But what you do have is an idea, a problem worth solving, and the courage to start.
Here Pre-seed funding is there to support founders during this phase. It helps to turn your ideas into something real: a basic product, a prototype, or an early version that can be tested.
What Is Pre-Seed Funding?
At this stage:
- The startup may not be registered yet
- The product is still in planning or early build
- The founder is experimenting and learning
The amounts raised in pre-seed are usually small. But the importance of this stage is huge. Decisions made here shape the future of the startup. This stage exists because building even a basic product needs time, tools, and focus. Without some financial support, many founders are forced to quit early.
Why This Stage Exists
Pre-seed funding exists to reduce personal risk for founders. When founders work full-time on an idea without support:
- Savings get drained
- Pressure increases
- Focus reduces
It is not about proving revenue.It is about proving direction.
Sources of Pre-Seed Funding
- Personal Savings
- Friends and Family
- Bootstrapping
Goals of the Pre-Seed Stage
Pre-seed is not about perfection.It is about learning fast.
Here are the key goals of this stage:
- Idea Validation
- MVP or Prototype
- Early Learning
What Founders Should Avoid at Pre-Seed Stage
Many founders make mistakes at this stage.
Avoid:
- Overbuilding features
- Spending on branding too early
- Hiring large teams
- Chasing big investors
Pre-seed is about focus. One clear problem. One simple solution.
When Is a Startup Ready for the Next Stage?
A startup is ready to move forward when these are clear:
- The problem is clearly defined
- Early users show interest
- The MVP works
- The founder understands the market better
Here at this point, the startup is ready for funding where the real validation begins.
Finding Product-Market Fit for Seed Funding
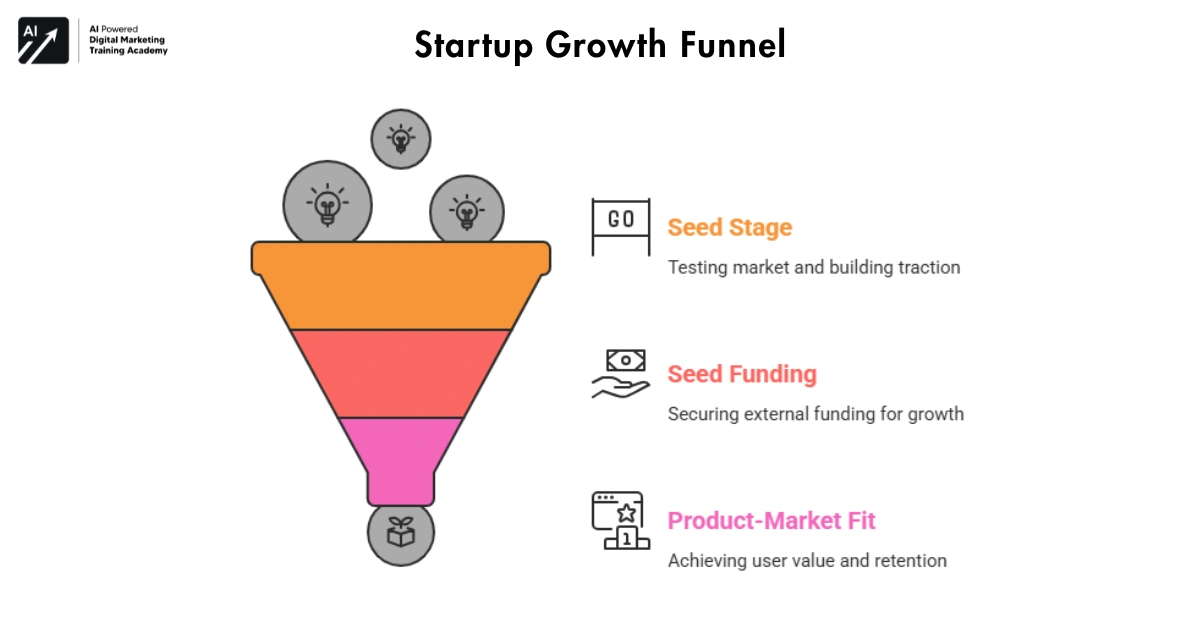
Once an idea is just validated and a basic product is there, a startup enters a new phase. This is the seed stage. At this point, the startup is no longer just an idea. Here it is taken first real steps.
What Is Seed Money?
Seed funding or seed money is the first official external funding round for many startups.
In simple words, seed funding helps startups:
- Improve the product
- Find early users
- Test pricing and positioning
- Build initial traction
This funding stage is called “seed” because it plants the base for future growth. If the seed is strong, the startup can grow into a real business.
Difference Between Seed and Pre-Seed Funding
In this time founders get confused between pre-seed and seed funding. The difference is so simple. Here is the explanation
At the seed stage:
- Risk is lower than pre-seed
- Expectations are higher
- Data matters more than ideas
- Investors just look for signals, not just for stories.
How Seed Funding Is Usually Used
Seed money is spent carefully.
Common uses include:
- Product improvement
- Hiring a small core team
- Basic marketing and outreach
- Tools and infrastructure
This is not the stage for luxury spending. Every rupee must bring learning or progress.
Common Seed-Stage Mistakes Founders Make
Some mistakes appear often at this stage:
- Scaling too early
- Ignoring user feedback
- Spending too much on marketing
- Copying competitors blindly
- Seed funding is not about speed.It is about direction.
- Wrong direction + money = faster failure.
When Is a Startup Ready for the Next Stage?
A startup is ready to move when:
- Users clearly value the product
- The problem-solution fit is proven
- Retention improves
- Growth shows consistency
This process is called product-market fit. Once you get this, the startup is almost ready for Series A funding, where the focus shifts from validation to building a real business.
Series A Funding – Building a Real Business
Reaching Series A is a big moment for any startup. It means one important thing. At this stage, the product works and the users are coming back, and the market response is positive.
The startup has moved past survival mode. Now the focus shifts to building a real, structured business. Series A funding exists to help startups move from “this works” to “this can scale.”
What Is Series A Funding?
Here it is the first major institutional funding round.
In simple words, it is raised when:
- Product-market fit is visible
- User demand is growing
- The business model makes sense
At this stage, investors are not betting on ideas. They are betting on execution.
Series A funding helps startups:
- Build strong teams
- Improve systems
- Expand reach
- Create predictable growth
This is where a startup starts behaving like a company.
Why Startups Raise Series A Funding
Here Startups helps the Series A not because they need money to survive, but because they need money to grow properly.
Growth brings new challenges:
- Managing people
- Handling customers at scale
- Improving technology
- Competing in the market
- Without funding, growth becomes slow and risky.
Series A gives founders the resources to grow without breaking the system.
When a Startup Is Ready for Series A
Not every startup is ready for Series A. Investors look for clear signals.
Common signs include:
- Strong user retention
- Consistent month-on-month growth
- Clear understanding of customers
- Repeatable sales or acquisition process
- A focused core team
How Series A Funding Is Used
Series A money is used to strengthen the foundation.
Team Expansion
Startups begin hiring beyond the founding team.
Common hires include:
- Engineers
- People Who Work in Sales and Marketing
- Operations and support staff
Hiring the right people at this stage is very important. One wrong hire can slow the whole business down.
Product Improvement
The product evolves based on real data.
Focus areas include:
- Performance
- User experience
- Reliability
- Feature refinement
The goal is to build a product users can depend on daily.
Marketing and Growth
Unlike the seed stage, marketing now becomes more structured.
Startups invest in:
- Proven acquisition channels
- Brand presence
- Partnerships
- Growth is planned, measured, and optimized.
Who Invests in Series A?
Series A investors are usually professional institutions.
- Venture Capital Firms
- Big Investment Organizations
At this stage, investors expect regular reporting, transparency, and discipline.
New Pressures at Series A Stage
Series A brings opportunity and pressure.
Founders face:
- Higher expectations
- Faster decision-making
- Investor accountability
- Team leadership challenges
Common Mistakes Founders Make at Series A
Some mistakes repeat often:
- Hiring too fast
- Ignoring culture
- Chasing growth without unit economics
- Losing focus on core users
- Series A is not about becoming big overnight.
- It is about becoming strong and reliable.
Preparing for the Next Stage
A startup is ready to move beyond Series A when:
- Growth is consistent and scalable
- Revenue model is clear
- Operations are stable
- Teams work independently
At this point, the startup enters Series B, where the goal is scaling aggressively.
Series B Funding Scaling the Business
By this time a startup can reach Series B, it has proven that the product works, the market exists, and the business model can generate revenue. Series B is all about scaling taking the business to new heights. In this stage there is no longer survival or early testing.
It’s just about increasing and building strong teams which help to improve processes, and preparing the company for long-term growth. At this stage investors look for startups that are ready to handle bigger challenges and dominate a larger market.
What is meant by Series B funding?
Series B funding is a stage where companies focus on growth. In simple words, it is money raised to:
- Expand the market
- Strengthen operations
- Increase revenue in a smart way
Series A proves the model, Series B scales it efficiently.
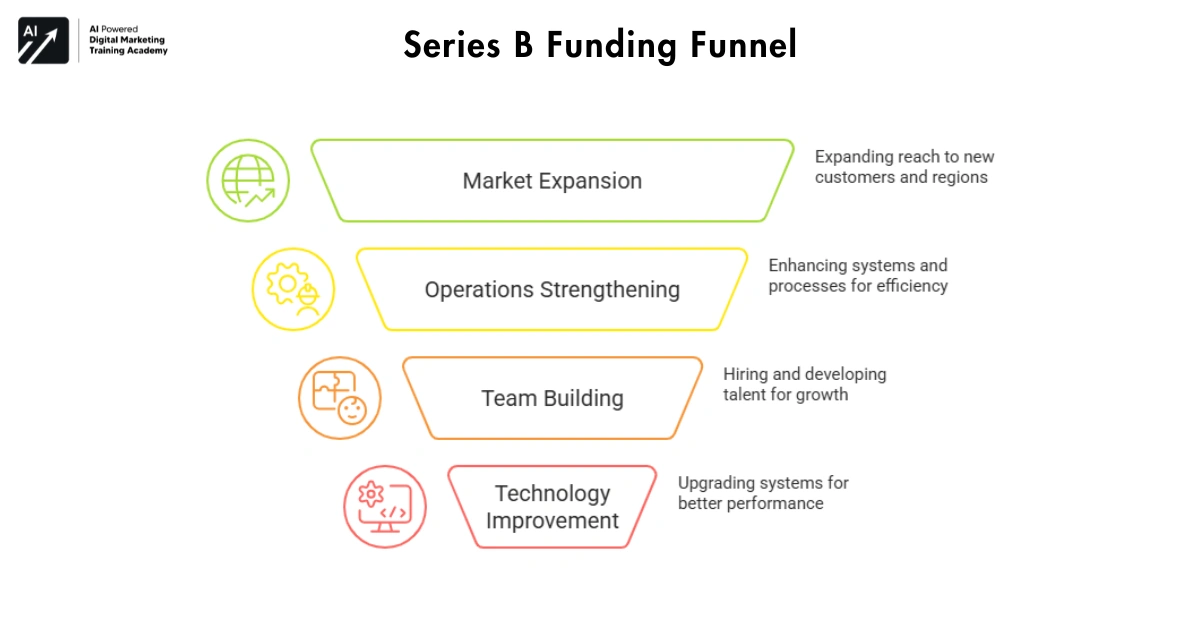
Goals of Series B Funding
The goals of Series B funding are focused on growth and efficiency:
- Market Expansion.
- Process Improvement
- Operations Strengthening
Common Series B Investors
Investors at Series B are more conservative but have deeper pockets.
- Large Venture Capital Firms
- Growth Investors
Specialized investors focusing on scaling companies. They look for businesses ready for significant expansion. Help companies grow internationally and prepare for an IPO
At this stage, investors care not only about revenue but also about profitability, market share, and long-term sustainability.
Challenges at Series B Stage
Scaling is never easy. Startups often face:
- Hiring challenges Like: Finding the right talent that matches the company’s culture and growth needs
- Operational gaps: Early systems may not support rapid scaling
- Market competition Like: Bigger players may start competing aggressively
- Cash flow management be like: Higher growth leads to higher spending
Series B funding needs smart planning to prevent growing too fast.
How Series B Funding Is Used
Series B money is spent on strategic growth:
- Increasing sales and also marketing teams
- Technology improves for efficiency
- Improving the customer service and retention
- Growing the business into new regions
- The goal is smart growth, not big spending.
Improving features of the product based on their market demand
Series C Funding: Building Market Dominance
At this point, startups are mature businesses aiming to strengthen their market position. Companies may use this Series C funding to get more competitors and prepare for an IPO. This is a high-risk way, and also a high-investment stage where success can shape the company’s future for years to come.
What Is Series C Funding?
Series C is the late-stage growth funding round for startups that have:
- Strong revenue streams
- Established products or services
- A loyal customer base
- Proof of scalability
In simple terms,this Series C funding is money raised to grow fast, expand internationally, and consolidate market leadership. The focus shifts from learning and building to dominating the market and maximizing value.
How Series C Funding Is Used
Series C funds are used strategically for large-scale moves:
International Expansion
- Launching products in new countries
- Localizing operations and marketing
- Establishing global teams and offices
Expanding this internationally to increase market size exponentially but also requires careful planning.
Acquisitions
- Buying competitors or complementary startups
- Integrating new technology, products, or talent
- Expanding customer base quickly
Acquisitions at this stage can accelerate growth faster than organic methods.
IPO Preparation
- Structuring financials and operations
- Building governance related frameworks
- Complying with regulatory requirements
Here series C funding usually sets the stage for a successful public offering.
Benefits of Series C Funding
Series C provides the resources to:
- Strengthen the brand globally
- Build leadership in the market
- Launch advanced technology or products
- Get ready for an IPO or planned exit
It also signals confidence to the market: if a startup raises Series C successfully, it is seen as a major player in its industry. Series C success sends a clear message: this startup is a major force in its industry.
Key Challenges in Series C
Challenges will continue, even at this advanced stage:
- Managing large teams across regions
- Protecting the company culture even the growth is more
- Successfully combining the acquired companies
Getting ready for a public offering
Series C which acts as the final step before going public.
Important steps include:
- Clean and verified financial records
- Experienced with skilled leadership team
- Solid legal compliance and governance structure
- Clear growth roadmap for investors
A successful Series C round makes the transition to IPO smoother and more predictable.
IPO – From Startup to Public Company
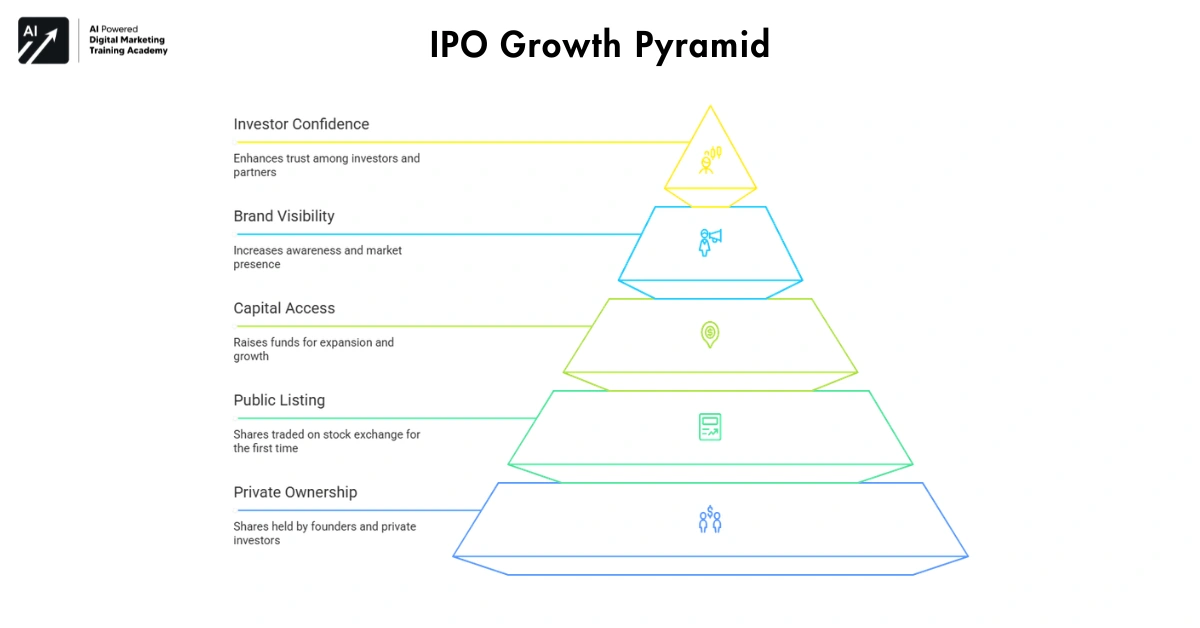
And finally, they reach their IPO (Initial Public Offering): This is the highest milestone for any budding start-‘up company. If a private company lists its shares on a stock exchange and they are available to trade by others in public trading for the first time, that event has been called an IPO since 1992. A private company becomes a public enterprise at this step.
Having an IPO opens the door to getting a lot of money, will also create a strongly recognized public brand and increase investors’ confidence in the company. But to Founders And early investors and employees an IPO means much more than capital it is many years of planning finally bearing fruit. Basically put, an IPO lets a company put its shares on the public stock market.
Before an IPO:
Only founders, employees, and private investors own shares in the company.
After an IPO:
Anyone can buy company shares, and the business becomes accountable to public shareholders. This process helps companies raise significant capital while giving early investors a chance to exit partially or fully.
Why Startups Go Public
Startups choose to go public for several important reasons:
- Access to Large Capital
- Private funding has limits.
An IPO can raise hundreds or even thousands of crores in one round.
- Brand Trust and Visibility
- Being listed on a stock exchange builds credibility.
Customers, partners, and suppliers often trust public companies more.0
Benefits of Going Public
An IPO offers long-term advantages:
Access to Large Capital
- Companies are able to generate enormous funds for expansion.
- Money can also be spent on R&D, hiring, and international growth.
Stronger Brand Trust
- The fact is that publicly traded firms are more reliable.
- Such an approach helps in building confidence levels in customers, vendors, and business partners
Greater Market Visibility
- An increase in awareness is also generated through the media coverage and along with the reports by stock analysts
- More visibility can lead to more sales and partnerships.
Employee Motivation
- Stock options become tradable, rewarding employees.
- Talent attraction improves as people prefer companies with public growth potential.
Conclusion – Choosing The Right Funding At The Right Time
An incorrect choice can lead to stalling or risking growth. With an apt funding source and at an apt time, business can gain momentum. Most founders tend to focus more on fundraising, hoping it is a measurement of success.
But raising this fund at a wrong time may lead to a few issues: Dilution of ownership Investor Pressure Unrealistic Growth Expectations High cash burn without results.
“Funding should reflect the actual needs of your start-up, not speed, but smart planning.“









